목차
Summary
이 게시물에서는 지난 게시물에서 소개한 Logrotate 기능 설명에 이어서 설정하는 방법을 알아보고자합니다.
만약 logrotate 기능에 대해서 이해하고자 한다면 아래 링크를 클릭해주세요.
[CentOS and Redhat Linux] - (CentOS7) 리눅스 Logrotate 기능(1)
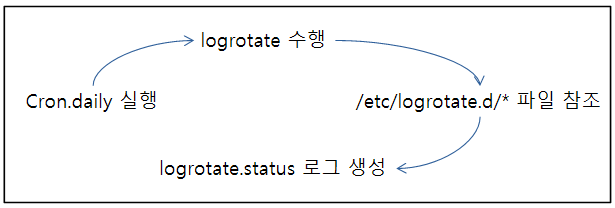
How can I set up the logrotate function?
Case 1 - /var/log 디렉터리 밑에 있는 로그 파일 관리
1. /etc/logrotate.conf 파일 내용 수정
# rotate log files weekly
weekly
# keep 4 weeks worth of backlogs
rotate 4
# create new (empty) log files after rotating old ones
create
# use date as a suffix of the rotated file
dateext
# uncomment this if you want your log files compressed
#compress
# RPM packages drop log rotation information into this directory
include /etc/logrotate.d위 설정대로 파일에 설정한 경우 1주일 주기로 4번 회전하므로
최근 4주치의 로그를 create 하여 보관하면서 생성되는 파일이름에 날짜(YYYYMMDD) 지정합니다.
2. /etc/logrotate.d 디렉터리에서 참조될 파일 확인
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/logrotate.d/
[root@localhost logrotate.d]# ls -al
합계 40
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 134 5월 28 10:07 .
drwxr-xr-x. 81 root root 8192 7월 14 16:06 ..
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 91 9월 30 2020 bootlog
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 93 4월 28 2021 firewalld
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 88 5월 19 2022 subscription-manager
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 302 12월 26 2022 syslog
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 100 3월 17 2021 wpa_supplicant
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 103 10월 2 2020 yum
3. Cron.daily 설정으로 자동 동작
[root@localhost cron.daily]# cd /etc/cron.daily/
[root@localhost cron.daily]# cat logrotate
#!/bin/sh
/usr/sbin/logrotate -s /var/lib/logrotate/logrotate.status /etc/logrotate.conf
EXITVALUE=$?
if [ $EXITVALUE != 0 ]; then
/usr/bin/logger -t logrotate "ALERT exited abnormally with [$EXITVALUE]"
fi
exit 0/etc/cron.daily/ 디렉터리에 logrotate 스크립트를 만들어 매일 00시 logrotate 기능이 자동으로 수행되게 됩니다.
하지만 테스트를 위해서 수동으로 하는 방법이 필요하니 수동 동작도 살펴봅시다.
4. logrotate 수동 동작
logrotate [-v] [-f] <설정파일>-v : 실행 과정을 자세히 표시합니다. (옵션)
-f : 강제 실행으로 모든 로그 파일을 회전시킵니다. (옵션)
<설정파일> : logrotate 설정 파일의 경로를 지정합니다. 기본적으로 /etc/logrotate.conf 파일이 사용됩니다.
예를 들어, 기본 설정 파일을 사용하여 'logrotate' 명령을 실행하려면 아래와 같이 사용할 수 있습니다
logrotate /etc/logrotate.conf
Case 2 - 원하는 디렉터리 로그 파일 관리
1. /etc/logrotate.d/[로그파일명]
vi /etc/logrotate.d/syslog
사용자가 추가한 로그 파일에 대한 rotate 지정시에는 파일에 지정해주어야 합니다.
예를 들어, syslog 파일을 rotate 실행해 보도록 하겠습니다.
(필요시 sftp, apache, mysql 등 원하는 파일을 생성)
/var/log/cron
/var/log/maillog
/var/log/messages
/var/log/secure
/var/log/spooler
{
weekly
missingok
rotate 52
compress
dateext
notifempty
sharedscripts
postrotate
echo "[`date`] Logrotate Success" >> /var/log/logrotate
/bin/kill -HUP `cat /var/run/syslogd.pid 2> /dev/null` 2> /dev/null || true
endscript
}/etc/logrotate.d/syslog 파일에 위와 같이 설정한 경우 1주일 주기로 52번 회전하므로
52주치의 로그를 관리하며, 생성할 때 파일의 size가 0이면 rotate 하지 않고 에러 메시지를 발생시키지 않습니다.
관련 스크립트들이 공유된 환경에서 실행되며, 파일 생성시 파일명에 날짜를 기록하고 압축합니다.
logrotate 실행이 완료 된 이후 postrotate 스크립트가 실행됩니다.
postrotate 블록은 /var/log/logrotate 파일에 결과를 로깅하며,
syslogd 서비스의 PID를 확인하여 HUP 시그널을 보내 로그파일을 다시 연결하도록 합니다.
2. logrotate 수동 동작
/usr/sbin/logrotate -f /etc/logrotate.d/syslogCase 1과 다르게 수동 동작할 파일명을 지정해주어야 합니다.
만약 /etc/logrotate.conf 파일을 그대로 실행하게 된다면
syslog 와 lorotate.conf 파일이 충돌하여 정상적으로 동작하지 않을 수 있습니다.
3) 설정한 결과를 확인
[root@localhost ~]# ls -al /var/log | grep 202307
-rw------- 1 root root 137 7월 14 17:01 cron-20230714.gz
-rw------- 1 root root 190 7월 14 17:01 messages-20230714.gzrotate 설정에 따라서 생성된 파일을 볼 수 있습니다.
나머지 파일들은 로그가 없어 rotate 되지 않은 모습입니다.
[root@localhost ~]# tail /var/log/logrotate
[2023. 07. 14. (금) 16:51:40 KST] Logrotate Success
[2023. 07. 14. (금) 16:51:47 KST] Logrotate Success
[2023. 07. 14. (금) 16:52:41 KST] Logrotate Successlogrotate 명령이 실행된 결과를 잘 로깅 하고 있음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
Conclusion
지난 게시물에 이어서 Logrotate 기능을 설정하고 적용한 뒤 확인하는 방법에 대해서 설명했습니다.
필요시 원하는 옵션과 원하는 로그 파일을 지정하여 각각의 로그 파일을 관리하도록 하는데 도움이 되었으면 합니다.
'CentOS and Redhat Linux > 보안설정' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Linux) CentOS7 방화벽(firewalld) 설정 (1) | 2023.11.20 |
|---|---|
| (CentOS7) 리눅스 Logrotate 기능(1) (1) | 2023.07.14 |
| (CentOS7) OpenSSL 버전 업그레이드 (1) | 2023.07.10 |


